What is Artificial Intelligence? The Complete Beginner’s Guide (2026)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a plot device for science fiction films or the subject of thick, boring academic tomes. In the year 2026, it is the invisible force propelling our world economy, individual productivity, and individual and collaborative scientific achievements. From the computer algorithms powering the social media sites you enjoy to the autonomous systems identifying novel life-saving medications, AI is now the technology of the 21st century.
This manual offers a complete in-depth look at what Artificial Intelligence (AI) is, how it functions, the history which has culminated in the present, and the choices that stand at the intersection that these systems are reaching with regard to their "agency."

Contents:
- Part 1. Defining Artificial Intelligence
- Part 2. A Simple History: The Seven-Decade Journey
- Part 3. The AI Hierarchy: Understanding the "Nesting Dolls"
- Part 4. The Three Levels of Intelligence
- Part 5. Real-World Use Cases: How AI Touches Your Life
- Part 6. The Ethics of Intelligence: Bias, Data, and Truth
- Part 7. Preparing for the AI-Augmented Future
Part 1. Defining Artificial Intelligence
In the most simplified definition, Artificial Intelligence is a field in the realm of computer science that is concerned with creating systems that are able to carry out tasks which will normally require human intelligence. Such tasks involve vision, speech, decision-making, and translation.

Shift from Logic to Learning
Traditionally, the computer software utilized a system of "if-then" logic. A programmer designed a program or a series of instructions, which the computer executed perfectly. If an unforeseen circumstance arose that the programmer did not program for, the computer program failed.
Modern day AI systems, on the other hand, operate differently. Rather than being programmed to follow rules, modern day AI systems are designed to learn. They employ mathematical models to predict patterns within massive amounts of data. By doing this, they become capable of operating in "unpredictable environments," which entails constantly fluctuating variables. An example of this would be navigating through a busy city or predicting markets.
The 2026 Definition: Agentic AI
As of 2026, the state of the industry is now past the era of "Generative AI" (content generation) to "Agentic AI." As opposed to the early stages of AI, which were reactive (where it would wait for a command and respond accordingly, such as the early versions of ChatGPT), Agentic AI systems are proactive. They are systems that are able to reason, plan, and complete multi-step tasks across multiple applications.
Part 2. A Simple History: The Seven-Decade Journey
A common way to portray the progress of AI is as a sequence of "summers" (years that were characterized by intense interest and large investments) and "winters" (years marked by disappointment and low interest). We live through the most substantial "AI Summer" ever.
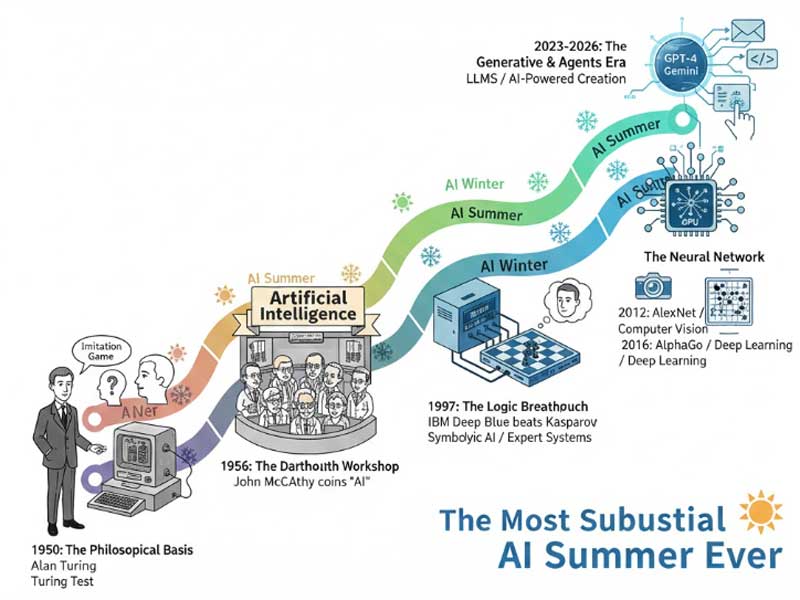
1950: The Philosophical Basis
It started with Alan Turing, the British mathematician who was also an accomplished code breaker. He came up with the "Imitation Game," now known as the Turing Test, when he published the paper "Computing Machinery and Intelligence." He suggested that when his machine was able to talk to a human in such a perfect manner that the human couldn't tell whether he or she was talking to the machine or the human itself, then the machine was capable of thinking.
1956: The Dartmouth Workshop
The Artificial Intelligence was coined officially by John McCarthy in the event of the summer research project on Artificial Intelligence at Dartmouth College. The event was attended by the founders of AI, and these founders envisaged that in a generation, apart from human beings, an intelligent machine would be invented.
1997 - The Logic Breakthrough
For many decades, "AI" meant "Symbolic AI" or "Expert Systems," where rules were carefully programmed by human coders. The height of this achievement was IBM's Deep Blue beating world chess champion Garry Kasparov. Though remarkable, Deep Blue did not "know" how to play chess. Instead, it relied on massive processing power to solve millions of paths via "brute force" computations.
2012–2016: The Neural Network
The dawn of modern AI began to emerge when scientists discovered that Neural Networks could actually be trained on high-performance Graphics Processing Units called GPUs.
• 2012: AlexNet transformed computer vision
• 2016: Google’s computer program called AlphaGo won a game of Go against Lee Sedol. It is different from the Deep Blue computer system in that AlphaGo utilized "Deep Learning" to gain the intuition of the game beyond that of a human’s.
2023–2026: The Generative and Agent
The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 and Google Gemini is a game changer in this landscape. AI is no longer a data analyzation tool; it's a data generation tool. We have entered the era of AI Agents in 2026. We not only write emails through AI; we also manage our mailboxes and carry out software code through AI.
Part 3. Understanding the AI Structure
In order to grasp AI, it is necessary to understand how these subfields of AI are related to each other. One way of doing this is to think of these subfields as a series of Russian nesting dolls.

Artificial Intelligence
This is the broad umbrella. This includes everything from the simplest thermostat in your home to the most sophisticated robot. Any method used to simulate human-like behavior in a computer qualifies under this category.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the engine that powers AI. Rather than teaching the computer the route, the computer is provided with the destination along with examples of how human drivers get to the destination. ML relies on statistics, which help the machine learn to perform a task better the more it is exposed to data.
• Supervised Learning: Learning from labeled examples (for example, "this is a picture of a cat").
• Unsupervised Learning: The system identifies hidden patterns within unlabeled data (like segmenting customers based on buying behavior).
Deep Learning (DL)
This is a specialized type of ML. It uses Artificial Neural Networks that are multi-layered (thus the term "deep"). Such networks are built to take after the functioning of the neurons in the human brain. It is Deep Learning that brought us the "magic" of the past decade, such as almost flawless voice recognition, facial recognition, or real-time translation.
Generative AI (The Innermost Doll)
Generative AI is a "specific application of Deep Learning." While conventional Deep Learning may be employed for image classification (Is this an image of a dog?); Generative AI is utilized for generating an image of a dog that is not known or existent yet. This is achieved through "Transformer" architectures, as these architectures can interpret the relationship of various pieces of data that form a coherent "sequence."
Technical Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) | Generative AI (GenAI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Data | Structured (Spreadsheets) | Unstructured (Video, Audio) | Massive Unstructured Datasets |
| Feature Extraction | Manual (Human-defined) | Automatic (By the model) | Contextual (By Transformer) |
| Primary Goal | Prediction/Classification | Pattern Recognition | Creation/Synthesis |
| Real-World Tool | Credit Scoring | FaceID / Siri | ChatGPT / Midjourney |
Part 4. The Three Levels of Intelligence
What’ s next for us? There are three phases of "smartness" that computer scientists use to describe the evolution of AI.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
This is the only kind of AI in existence at present. ANI stands for Artificial Narrow Intelligence. ANI is a "narrow" intelligence because it is set up to be the best at one task. It might be superior to any physician in diagnosing lung cancer from an X-ray, but not at playing a game of checkers or composing a poem. Every computer system in existence, including the most sophisticated LLMs, qualifies as a form of Narrow AI because they work within a set mathematical paradigm of "next-token prediction."
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
"The Holy Grail" of AI research is known as AGI. It is a "machine that has the capacity to comprehend, learn, and apply its intellect to any cognitive task that a human can perform." An AGI "could educate itself on physics, cook a gourmet meal, or draft a legal brief—all without being specifically programmed to accomplish any of those activities."
In 2026, estimates as to when we shall attain "The Holy Grail" vary wildly among those with expertise—from 5 to 20 years.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
"ASI" refers to the hypothetical "Future" wherein A.I. outperforms human intelligence in every aspect and field—to include logic and mathematics, as well as social acuity, artistic expression, and even "emotional intelligence." It is the realm that science fiction occupies, but is fraught with deep philosophical implications vis-à-vis the "Future" of the human race.
Part 5. Real-World Use Cases: How AI Touches Your Life
"It is now clear that AI has shifted from demo-driven activities to becoming a 'quiet infrastructure' in its own right, becoming invisible in its drive to make our lives easier. AI is no longer an add-on product in our lives; rather, it is an invisible layer that is seamlessly incorporated into our homes, cars, and offices to make our work easier."
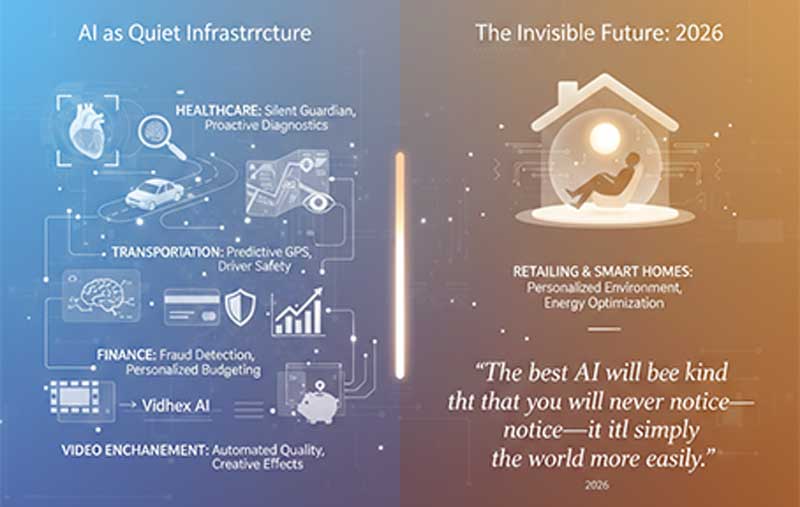
In the healthcare industry, AI serves as a "silent guardian" whereby the algorithms for diagnostics are able to scan imaging results for potentially life-threatening abnormalities. AI's ability to interpret vast amounts of data enables us to move towards a future of proactive healthcare, before the physical symptoms develop.
The efficiency of AI can also be noted in transportation, where GPS systems are able to predict the formation of traffic patterns even before they occur. Not only are GPS systems capable of determining routes, but cars today are employing computer visions and biometric systems to identify driver fatigue and mitigate accidents accordingly.
In finance, machine learning is hard at work with every use of your credit card, processing vast amounts of data in a matter of seconds to detect fraudulent activity. The same technology is used in personal finance applications that provide tailored advice on budgeting and investments based on your lifestyle.
AI is transforming how videos are created, edited, and enhanced by using machine learning to improve quality, automate edits, and generate creative effects. Tools like Vidhex AI Video Enhancer use advanced neural networks to sharpen details, reduce noise, and upscale resolution with minimal user effort. As AI continues evolving, video workflows are becoming faster, more accessible, and capable of results that once required expert skills and hours of manual work.
In the realm of retailing and smart homes, AI gives you a personalized environment that foretells when you will run out of what you need or automatically optimizes energy usage according to your schedule. In 2026, "the best AI will be the kind that you will never notice—it will simply make the world more easily."
Part 6. The Ethics of Intelligence: Bias, Data, and Truth
The increasing integration of AI into every aspect of our existence also demands that we solve what has been dubbed the "Black Box" problem: namely, the AI developers themselves do not always fully understand how a particular decision is made.

The Problem of Bias
AI models are being trained on human-created data. This implies that AI models possess the worst characteristics of human beings.
• Racial Bias: It has been found that facial recognition algorithms could encompass a 35% error rate for darker-skinned females and a rate of less than 1% for lighter-skinned males.
• Socioeconomic Bias: If a machine learning system for hiring is based on a dataset from a company where they only recruited men, this system can learn from this experience and understand that only males can apply for a particular job.
The "Hallucination" Factor
"Source of truth" is not something that can be found in Generative AI. It is a probability machine. It will cause "hallucinations"—cases when the AI is sure about the data that is actually wrong. In 2026, one of the toughest challenges for the industry is to improve "grounding" of AI within real-world facts.
Deepfakes and Information Integrity
With the capacity of AI to produce hyper-real images and voice "clones," the realm of trust has entered into a crisis. In the years 2024 and 2025, the planet experienced an enormous rise in the "Deepfake" form of political advertising and frauds. With the advent of ease of access, the distinction between the "real" and the "synthetic" is becoming increasingly hazy.
Part 7. Preparing for the AI-Augmented Future
The "AI will take my job" fear is a familiar one. But any given expert will tell you they do not think the truth is necessarily this straightforward. They do not think AI will necessarily replace human jobs, but rather make them easier.

Key Skills for 2026 and Beyond:
Artificial Intelligence Literacy: Learning how to utilize AI tools such as "Prompt Engineering" for improving your output.
Critical Thinking: The capacity to check and evaluate AI-produced information.
Soft Skills: Empathy, negotiation, and complex leadership, which are still very difficult for artificial intelligence
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a mirror. It reflects our collective knowledge, our creative potential, and our biases. As we enter further into the year 2026, the vision is no longer to create systems that replace us but to create tools that aid us in solving the world’s biggest challenges, from climate change to diseases like cancers.
"The Complete Beginner" of today will become "The AI Collaborator" of tomorrow. With this understanding of the mechanics, history, and ethics behind this technology, you will be able to intelligently navigate a world where intelligence is no longer an exclusively human construct.